An overview of gout
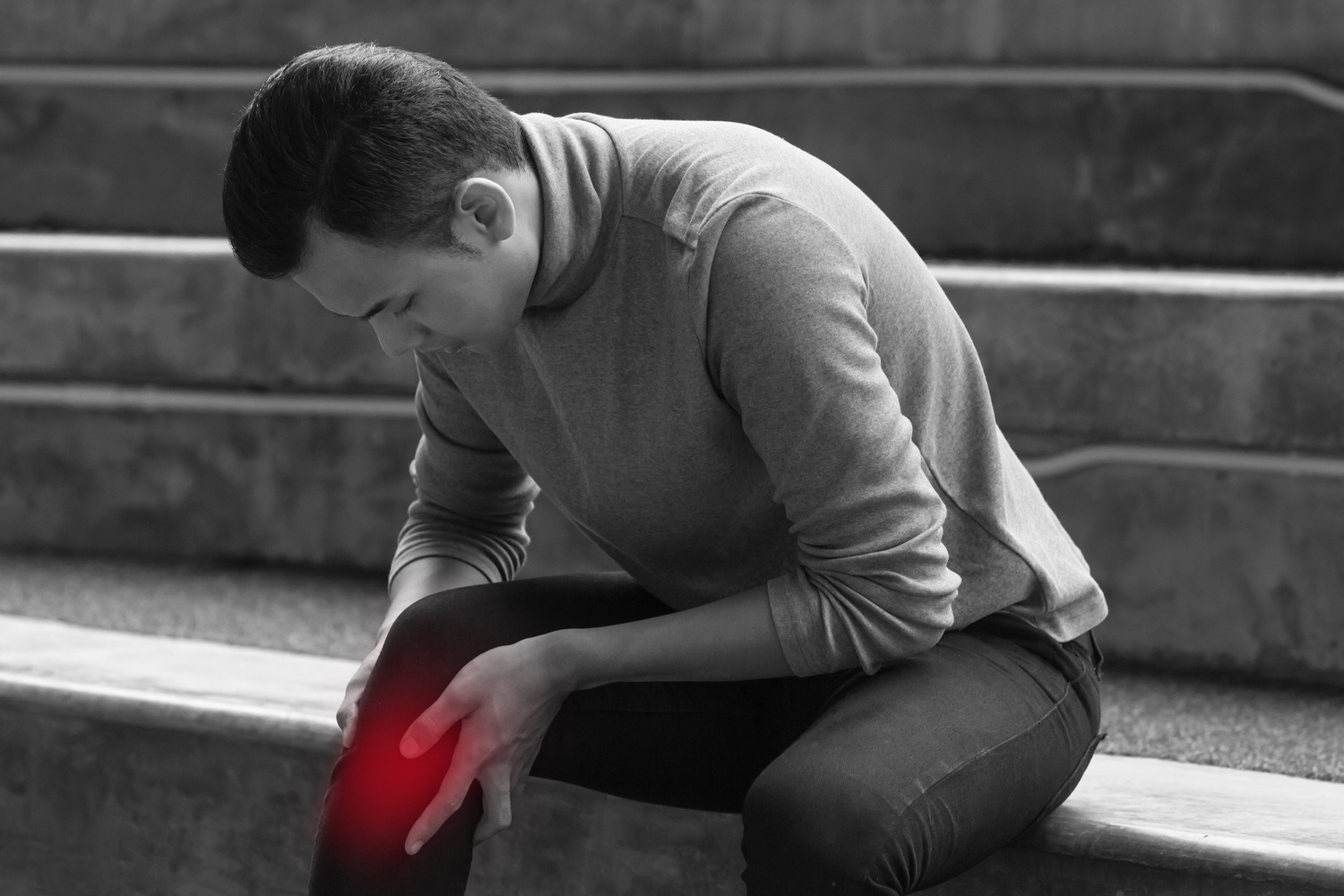
Gout is an aching and potentially disabling form of arthritis that causes inflammation in the joints that begins suddenly. It is caused by the crystals of uric acid in joints. The severe form of gout could sometimes affect many joints at once and is called as polyarticular gout.
Symptoms and signs
The first symptoms are, usually, intense episodes of painful swelling in single joints, especially the big toe and nodules under the skins that are known as Tophi. The swollen site may be warm and red in color.
Causes
When a high amount of uric acid, which is a normal waste product of the body, collects and forms a needle‐like urate crystal deposits in the joints, gout occurs. When the production of uric acid increases, the kidneys cannot remove it from the body completely. There are certain foods and drugs that may raise the uric acid levels and could steer to gout attacks. This food includes red meat, alcohol in excess amount, and the sugary drinks and foods that are rich in fructose. The increased uric acid levels in the blood may rise to create deposits of urate crystals in and around the joints. This can attract WBCs, leading to severe and painful gout attacks and very chronic arthritis. It also deposits in the urinary tract, which causes kidney stones.
The complications of a gout attack and chronic arthritis occur mostly in men. They may affect women after menopause, and they also affect the people having kidney diseases. It is linked to obesity, hypertension, chronic renal failure hyperlipidemia, and diabetes. It rarely affects children.
Risk factors
There are several risk factors of this disease. It affects people more commonly after surgery, dehydration, and trauma. Known as diuretics, the medication that treats high blood pressure and raises the level of uric acid in the bloodstream is a risk for gout. The medicines that lower the level of uric acid in the bloodstream can also cause a flare of gout. The low dose of aspirin can be impulsive in gout attacks. When cancer cells are destroyed, they can cause gout because of high levels of uric acid release.
Diagnosis
Doctors and specialists expect gout when a patient has joint swelling and intense pain in one or two joints at first, followed by times between these attacks when the patient doesn’t feel pain. The diagnosis of gout depends on finding the deposition of crystals under the skin. The crystals that are found as deposits and appear under the skin are called tophi and affect a person in advanced gout. The uric acid levels in the blood are important to measure, but they can sometimes be very acute. The X-rays might show joint damages in a patient who has been suffering from gout for a long time. Ultrasound and dual-energy computed tomography can also show the involvement of gouty joints, and these technologies can help in the diagnosis.
Home remedies
Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like naproxen sodium can be useful when there are no contradictions for decreased kidney function or stomach ulcers. Drinking plenty of water can be beneficial in preventing gout attacks.