Causes and risk factors of skin cancer
Skin cancer is a severe medical condition where abnormal cells develop on the epidermal layer. Areas exposed to the sun are more susceptible to this skin condition. There are four principal types of skin cancer – basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, and nonmelanoma skin cancer. Common symptoms include flesh-colored or brown lesion that does not go away, bleeding sore that heals up only to return in a few days, waxy bump, development of new asymmetrical moles, and lesion having an uneven or ragged outline with a diameter more than quarter-inch. The chances of skin cancer diminish by limiting the exposure to ultraviolet rays. Regular screening and timely detection help in the successful treatment of this condition.
Causes of skin cancer
Detailed below are some of the causes of skin cancer.
Mutations in DNA
One of the most significant causes of malignancy in skin cells is mutations in the DNA of epidermal cells. The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin and under normal circumstances, it continually gives rise to new cells by division. When there is a change in their chromosomal structure due to mutation, it produces an uncontrolled mass of abnormal cells.
UV exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are harmful energy emitted by the sun. It causes considerable skin damage, premature aging, and even skin cancer. Human beings can neither see these rays nor feel it, which makes them more prone to skin damage. Experts recommend use of broad-spectrum (protecting against both UVA and UVB) sunscreen with Sun Protection Factor (SPF) above 30 before going out in the sun for protection.
Exposure to carcinogenic chemicals
There are some chemicals which may lead to malignancy (especially squamous cell skin cancer) when individuals come in contact with them for an extended period.
Risk factors of skin cancer
Here are some of the risk factors for skin cancer.
Fair skin
Chances of developing skin cancer increases for fair-skinned people. They have less melanin (pigment imparting color to the skin) and thus inadequate protection against the harmful UV rays. The same is true for those having blonde hair, light-colored eyes, and freckled skin.
History of sunburn
Those who have experienced episodes of blistering sunburn either in their childhood or in teenage have a higher probability of developing skin cancer.
Excessive sun exposure
People spending long duration under the sun are more susceptible to malignancy in the skin. It is especially true if the skin does not remain protected by sunscreen or layers of clothing. Exposure to tanning lamps or beds can also induce the same response.
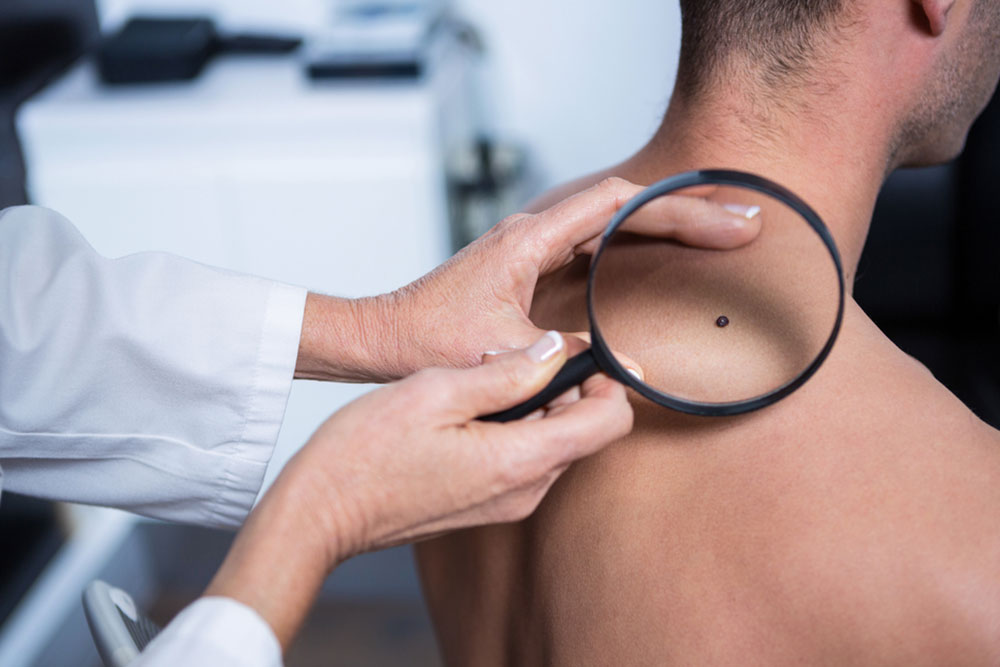
Moles
Individuals having multiple or abnormal shaped moles are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer. Oncologists recommend regular screening of these moles, especially if they are more than a quarter inch in diameter, as they tend to become malignant.
The above were the causes and risk factors of skin cancer. In addition to these factors, having a family history of malignancy in the skin, or a personal history of cancer also makes a person more susceptible to this condition.